“How is JavaScript asynchronous and single-threaded ?” The short answer is that JavaScript language is single-threaded and the asynchronous behaviour is not part of the JavaScript language itself, rather they are built on top of the core JavaScript language in the browser (or the programming environment) and accessed through the browser APIs.
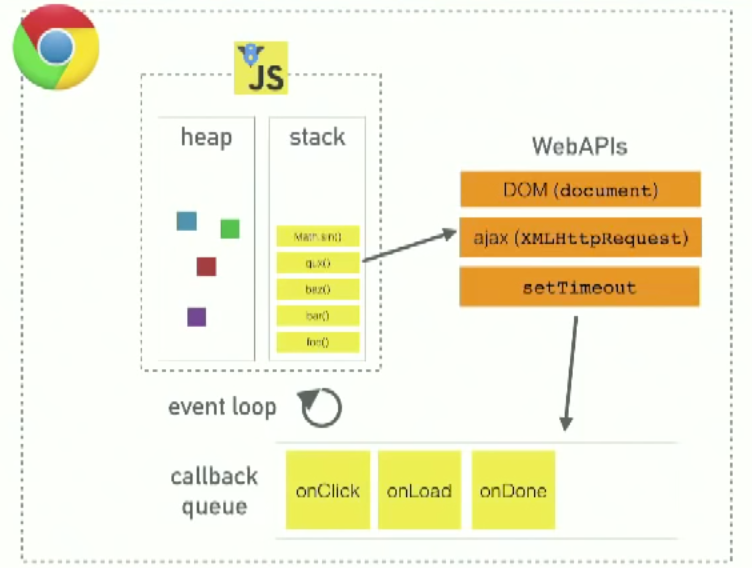
Heap - Objects are allocated in a heap which is just a name to denote a large mostly unstructured region of memory
Stack - This represents the single thread provided for JavaScript code execution. Function calls form a stack of frames (more on this below)
Browser or Web APIs are built into your web browser, and are able to expose data from the browser and surrounding computer environment and do useful complex things with it. They are not part of the JavaScript language itself, rather they are built on top of the core JavaScript language, providing you with extra superpowers to use in your JavaScript code.
Understand EventLoop with Example
function main(){
console.log('A');
setTimeout(
function display(){ console.log('B'); }
,0);
console.log('C');
}
main();
// Output
// A
// C
// B
Here we have the main function which has 2 console.log commands logging ‘A’ and ‘C’ to the console. Sandwiched between them is a setTimeout call which logs ‘B’ to the console with 0ms wait time.
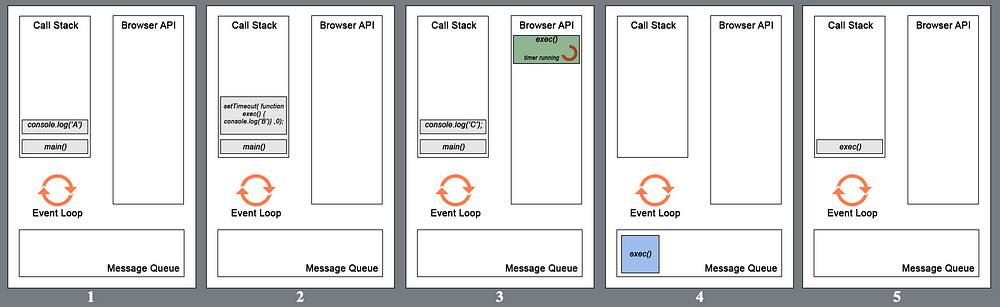
1. The call to the main function is first pushed into the stack (as a frame). Then the browser pushes the first statement in the main function into the stack which is console.log(‘A’). This statement is executed and upon completion that frame is popped out. Alphabet A is displayed in the console.
2. The next statement (setTimeout() with callback exec() and 0ms wait time) is pushed into the call stack and execution starts. setTimeout function uses a Browser API to delay a callback to the provided function. The frame (with setTimeout) is then popped out once the handover to browser is complete (for the timer).
3. console.log(‘C’) is pushed to the stack while the timer runs in the browser for the callback to the exec() function. In this particular case, as the delay provided was 0ms, the callback will be added to the message queue as soon as the browser receives it (ideally).
4. After the execution of the last statement in the main function, the main() frame is popped out of the call stack, thereby making it empty. For the browser to push any message from the queue to the call stack, the call stack has to be empty first. That is why even though the delay provided in the setTimeout() was 0 seconds, the callback to exec() has to wait till the execution of all the frames in the call stack is complete.
5. Now the callback exec() is pushed into the call stack and executed. The alphabet C is display on the console. This is the event loop of javascript.
So the delay parameter in setTimeout(function, delayTime) does not stand for the precise time delay after which the function is executed. It stands for the minimum wait time after which at some point in time the function will be executed.
https://medium.com/front-end-weekly/javascript-event-loop-explained-4cd26af121d4

Heap - Objects are allocated in a heap which is just a name to denote a large mostly unstructured region of memory
Stack - This represents the single thread provided for JavaScript code execution. Function calls form a stack of frames (more on this below)
Browser or Web APIs are built into your web browser, and are able to expose data from the browser and surrounding computer environment and do useful complex things with it. They are not part of the JavaScript language itself, rather they are built on top of the core JavaScript language, providing you with extra superpowers to use in your JavaScript code.
Understand EventLoop with Example
function main(){
console.log('A');
setTimeout(
function display(){ console.log('B'); }
,0);
console.log('C');
}
main();
// Output
// A
// C
// B
Here we have the main function which has 2 console.log commands logging ‘A’ and ‘C’ to the console. Sandwiched between them is a setTimeout call which logs ‘B’ to the console with 0ms wait time.

1. The call to the main function is first pushed into the stack (as a frame). Then the browser pushes the first statement in the main function into the stack which is console.log(‘A’). This statement is executed and upon completion that frame is popped out. Alphabet A is displayed in the console.
2. The next statement (setTimeout() with callback exec() and 0ms wait time) is pushed into the call stack and execution starts. setTimeout function uses a Browser API to delay a callback to the provided function. The frame (with setTimeout) is then popped out once the handover to browser is complete (for the timer).
3. console.log(‘C’) is pushed to the stack while the timer runs in the browser for the callback to the exec() function. In this particular case, as the delay provided was 0ms, the callback will be added to the message queue as soon as the browser receives it (ideally).
4. After the execution of the last statement in the main function, the main() frame is popped out of the call stack, thereby making it empty. For the browser to push any message from the queue to the call stack, the call stack has to be empty first. That is why even though the delay provided in the setTimeout() was 0 seconds, the callback to exec() has to wait till the execution of all the frames in the call stack is complete.
5. Now the callback exec() is pushed into the call stack and executed. The alphabet C is display on the console. This is the event loop of javascript.
So the delay parameter in setTimeout(function, delayTime) does not stand for the precise time delay after which the function is executed. It stands for the minimum wait time after which at some point in time the function will be executed.
https://medium.com/front-end-weekly/javascript-event-loop-explained-4cd26af121d4
No comments:
Post a Comment